Linux (Live-ISO)
Live-ISO installers usually contain the full set of requirements for installing an operating system as well as extra content for optional features. These images are much heavier than cloud-images and are generally 2-8Gb in size. Unlike cloud-images, Live-ISO installers can also be used to image physical machines and are suited for use in long-lived virtual-private servers.
Download or create an ISO file:
For Ubuntu images, tools like Cubic or PXEless can be used to create customized ISO installers.
When using Debian 12 as the source image, you may need to manually add a boot-entry to the virtual-machine bios after installation. That process is shown in-detail here: proxmox.com/wiki/OVMF/UEFI_Boot_Entries
Official Ubuntu and Debian images can be downloaded from:
Ubuntu:
- https://mirror.mijn.host/ubuntu-releases/22.04.3/ubuntu-22.04.3-live-server-amd64.iso
Debian12:
- https://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/current/amd64/iso-dvd/debian-12.1.0-amd64-DVD-1.isoDownload the ISO file
export IMAGE_URL="https://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/current/amd64/iso-dvd/debian-12.1.0-amd64-DVD-1.iso"
export IMAGE_NAME=$(basename -- "$IMAGE_URL")
wget -c -O "$IMAGE_NAME" "$IMAGE_URL" -q --show-progress
VM Setup
Configure the Virtual Machine options
# The name of the Virtual Machine
export VM_NAME="gameci"
# Number of physical CPU cores to allocate to the VM
export PHYSICAL_CORES="2"
# Number of threads per core.
# Set this to `1` for CPUs that do not support hyper-threading
export THREADS="1"
export SMP=$(( $PHYSICAL_CORES * $THREADS ))
# Amount of Disk Space to allocate to the VM.
# Cannot exceed available on host.
export DISK_SIZE="32G"
# Amount of RAM to allocate to the VM.
# Cannot exceed available RAM on host.
export MEMORY="8G"
# IP address where host may be reached. Do not use `localhost`.
export HOST_ADDRESS="SOME IP HERE"
# Port used by SSH on the host
export HOST_SSH_PORT="22"
# Port to use when forwarding SSH to the VM
export VM_SSH_PORT="1234"
# Port number to expose on the host for VNC
export VNC_PORT="0"Create an empty disk where the OS will be installed.
qemu-img create -f qcow2 disk.qcow2 $DISK_SIZE &>/dev/null
Create the VM
Create new guest:
sudo qemu-system-x86_64 \
-machine accel=kvm,type=q35 \
-cpu host,kvm="off",hv_vendor_id="null" \
-smp $SMP,sockets=1,cores="$PHYSICAL_CORES",threads="$THREADS",maxcpus=$SMP \
-m "$MEMORY" \
-cdrom $IMAGE_NAME \
-object iothread,id=io \
-device virtio-blk-pci,drive=disk,iothread=io \
-drive if=none,id=disk,cache=none,format=qcow2,aio=threads,file=disk.qcow2 \
-device intel-hda \
-device hda-duplex \
-serial stdio -vga virtio -parallel none \
-device virtio-net-pci,netdev=network \
-netdev user,id=network,hostfwd=tcp::"${VM_SSH_PORT}"-:"${HOST_SSH_PORT}" \
-bios /usr/share/ovmf/OVMF.fd \
-usbdevice tablet \
-vnc "$HOST_ADDRESS":"$VNC_PORT"Boot existing guest:
sudo qemu-system-x86_64 \
-machine accel=kvm,type=q35 \
-cpu host,kvm="off",hv_vendor_id="null" \
-smp $SMP,sockets=1,cores="$PHYSICAL_CORES",threads="$THREADS",maxcpus=$SMP \
-m "$MEMORY" \
-object iothread,id=io \
-device virtio-blk-pci,drive=disk,iothread=io \
-drive if=none,id=disk,cache=none,format=qcow2,aio=threads,file=disk.qcow2 \
-device intel-hda \
-device hda-duplex \
-serial stdio -vga virtio -parallel none \
-device virtio-net-pci,netdev=network \
-netdev user,id=network,hostfwd=tcp::"${VM_SSH_PORT}"-:"${HOST_SSH_PORT}" \
-bios /usr/share/ovmf/OVMF.fd \
-usbdevice tablet \
-vnc "$HOST_ADDRESS":"$VNC_PORT"
Connect via VNC
In your VNC software, use the address format
$HOST_ADDRESS:$VNC_PORTto connect to the VM.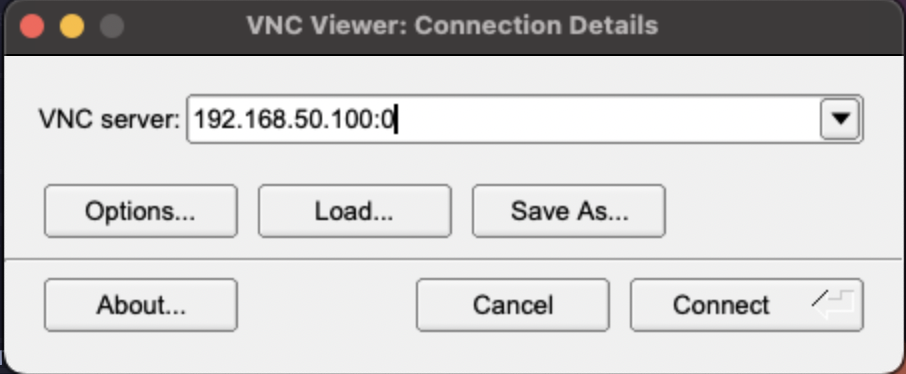
Complete the installation
Follow the instructions for Debian/Ubuntu installation using the guides in the Bare-Metal section.